Sezione in aggiornamento
Il Programma nazionale esiti (PNE)
Il Programma nazionale esiti (PNE) è uno strumento sviluppato da Agenas per valutare l’efficacia, l’appropriatezza e la sicurezza degli interventi sanitari, finalizzato al miglioramento della qualità delle cure e dell’equità di trattamento nel Servizio sanitario nazionale, a prescindere dall’area geografica di residenza, dal genere e dalla cittadinanza della persona.

Il Pne utilizza 195 indicatori basati su evidenze scientifiche, di cui:
- volumi di ricoveri per singolo istituto in 12 aree cliniche (cardiovascolare, cerebrovascolare, digerente, malattie infettive muscolo-scheletrico, oncologia, otorinolaringoiatria, pediatria, perinatale, respiratorio, trapianti, urogenitale)
- esito clinico in termini di mortalità (per esempio, la mortalità a 30 giorni dall’ammissione in ospedale per ictus ischemico o infarto miocardico acuto) e riospedalizzazione per complicanza
- tempestività (per esempio, l’intervento chirurgico entro 48 ore per frattura del collo del femore nei pazienti anziani)
- appropriatezza della procedura (per esempio, del taglio cesareo o della rimozione delle tonsille)
- numero di ricoveri in ospedale evitabili (dovuti alla carenza di assistenza sul territorio)
- accessi impropri al pronto soccorso (dovuti alla carenza di assistenza sul territorio)
- esiti a lungo termine (mortalità a un anno per complicanze dopo un infarto miocardico acuto o un ictus)
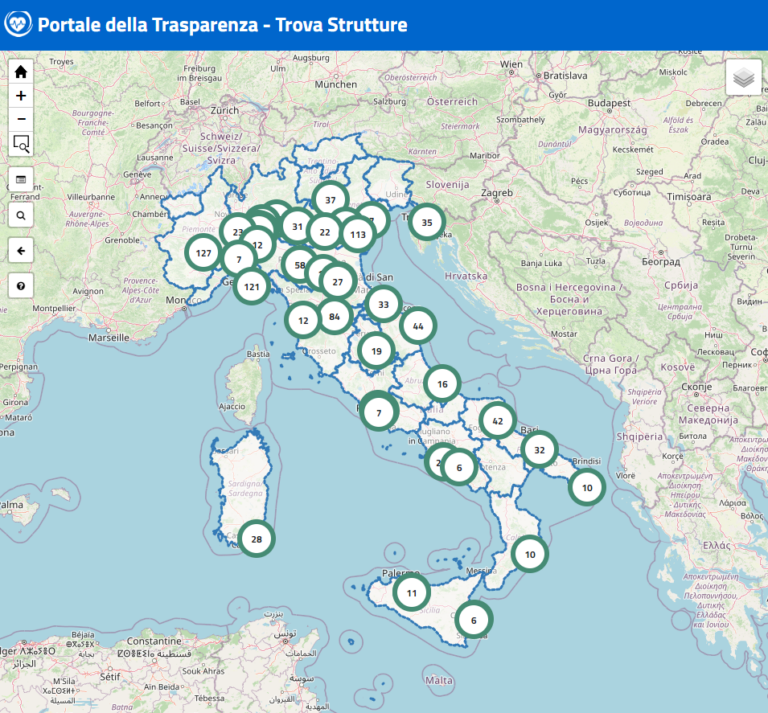
Mappa gli indicatori
Attraverso lo strumento Trova strutture è possibile consultare 55 indicatori del Pne riferiti a circa la metà degli oltre 90 interventi e ricoveri ospedalieri programmabili e senza carattere di urgenza inseriti nel portale.
Per ogni intervento, individuato sia tra quelli analizzati dal Pne sia tra quelli più frequenti dell’attività ospedaliera, è presente il numero di ricoveri all’anno per istituto.
Per alcune procedure vengono calcolati:
- la riammissione ospedaliera a 30 giorni per complicanza (ad esempio, per la riacutizzazione della broncopneumopatia cronica ostruttiva)
- il reintervento entro 6 mesi (ad esempio, per l’artroscopia del ginocchio)
- la revisione a 2 anni (ad esempio, per l’intervento di protesi all’anca).